Welcome to diabetes health. Online
Vision
Your eyes are the sensory organs that allow you to see. Your eyes capture visible light from the world around you and turn it into a form your brain uses to create your sense of vision. Your brain does not have sensory abilities of its own.
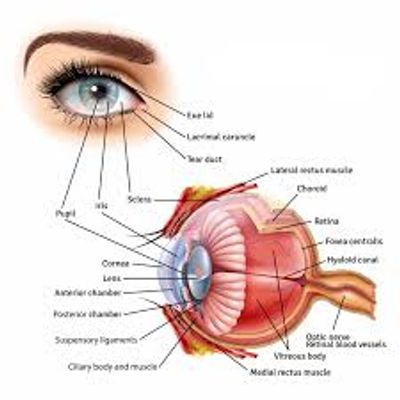
Different parts of the eyes
The Cornea
The Cornea is the clear, dome-shaped front part of the eye that bends light to help focus.
The Iris
The Iris is the colored part of the eye that controls how much light enters the eye by adjusting the size of the pupil.
The Pupil
The Pupil is the black circle in the center of the iris that allows light to enter the eye.
The Lens
The Lens is the clear part of the eye behind the iris that focuses light onto the retina.
The Retina
The Retina is the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye that converts light into electrical impulses.
The Optic nerve
The Optic nerve is the largest sensory nerve in the eye that carries the electrical impulses from the retina to the brain.
The Macula
The Macula is a small, sensitive area in the center of the retina that provides central vision.
The Fovea
The Fovea is at the center of the macula that provides sharp central vision.
The Sclera
The Sclera is the white part of the eye that gives the eyeball its shape and structure.
The Conjunctiva
The Conjunctiva is the clear, thin layer that covers the sclera and lines the inside of the eyelids.
Tears
The Tears are secreted by the tear glands, and they are responsible for lubricating the cornea, keeping the eye moist, and protecting it from injury and infection.
What is the connection between diabetes and the eyes?
Diabetic retinopathy: This is the leading cause of blindness in working-age adults. It is caused by high blood sugar damaging the blood vessels in the retina, which can lead to blurry vision, leaking, and bleeding.
Macular edema: This is swelling of the macula, which is the center of the retina and is responsible for sharp vision. It can cause blurred or distorted vision.
Cataracts: This is a cloudy buildup in the lens of the eye.
Glaucoma: This is damage to the blood vessels in the front of the eye, which can block the drainage of fluid.
Swollen lens: This can be caused by quick changes in blood sugar levels.
Other symptoms of eye problems related to diabetes include:
Headaches
Eye aches or pain
Watery eyes
Halos around lights
Dark areas or vision loss
Poor color vision
Spots or dark strings (floaters)
Flashes of light
To correct blurred vision caused by high blood sugar, you need to get your blood sugar back into the target range.
What are the necessary nutrients to keep your eyes healthy.
Nutrients necessary to keep your eyes healthy are Vitamin A (retinol), Vitamin C (ascorbic acid), Omega 3 fatty acids, Alpha-linolenic acid, Leucine, Zeaxanthin, Zinc and Vitamin E (Tocopherol)
This website uses cookies.
We use cookies to analyze website traffic and optimize your website experience. By accepting our use of cookies, your data will be aggregated with all other user data.